Barometric pressure, also known as air pressure, is the force or weight of the air around us. It can cause headaches, joint pain and fatigue.
- 1,201 - 1,400 hPA
- 1.001 - 1.200 hPA
- 700 - 1,000 hPA
Origin
the force exerted by air molecules when they press on the earth and all other surfaces
Effects
can cause headaches, joint pain and fatigue; radon levels can rise due to the negative pressure in the building
Improvement measure(s)
Improve ventilation
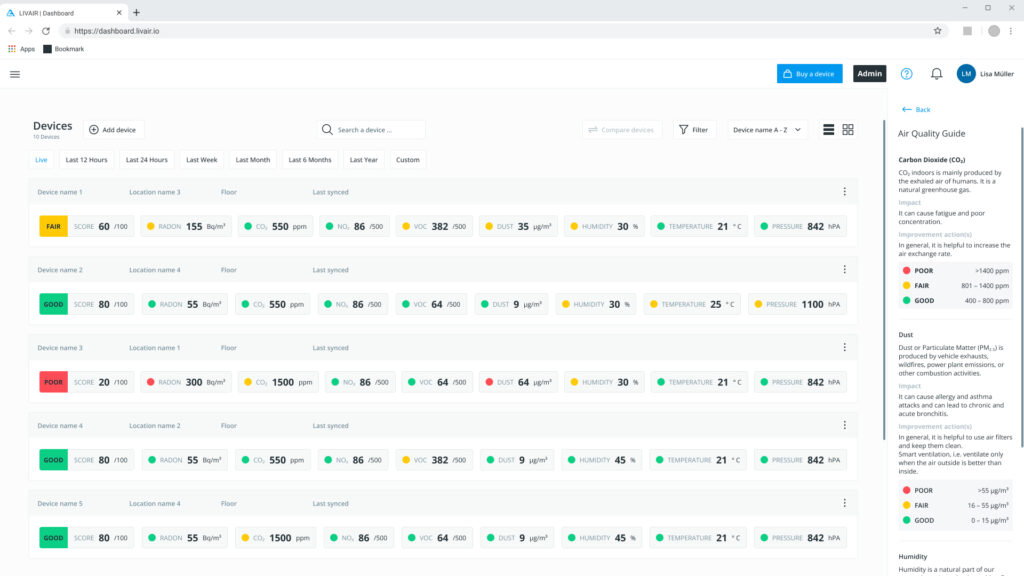

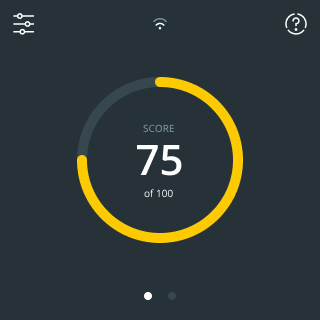
You can find all your real-time results in our dashboard with integrated air quality guide
The Air Quality Guide (AQG) is designed to help users quickly and easily classify their measured air values on a scale.
It will inform you about the origin of the relevant air factor, what effects it can have on your health and well-being and give you some general improvement measures that can work if you don't have complex problems.
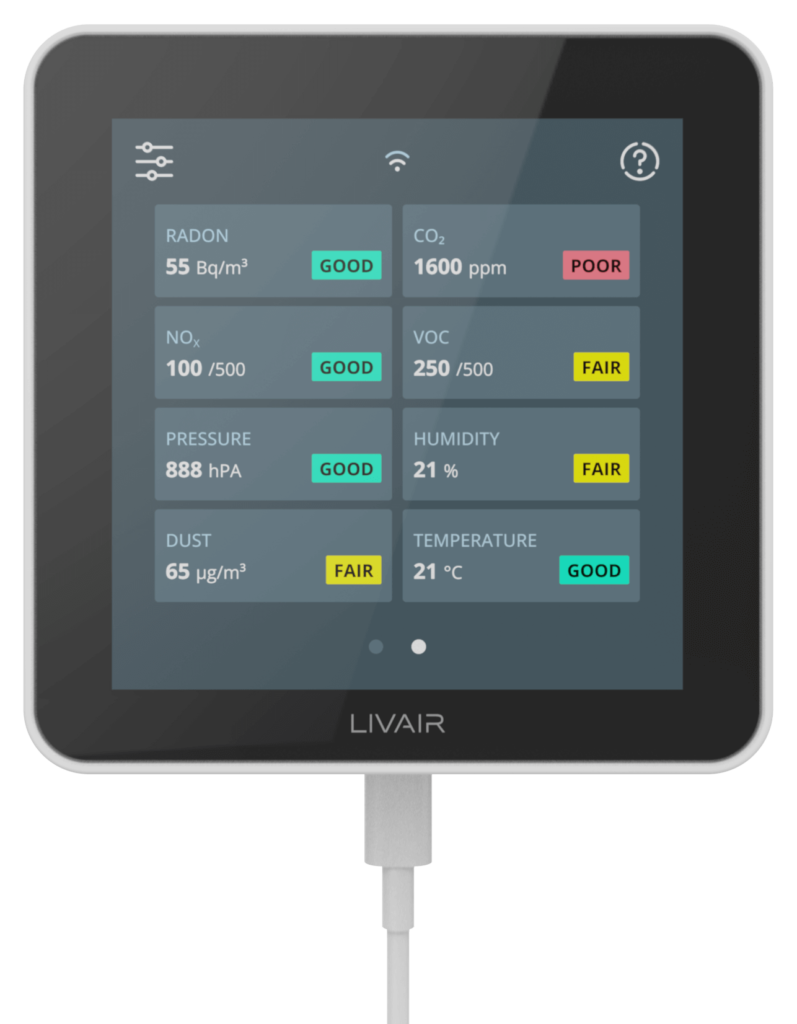
LivAir One - the most intelligent air quality monitor
The LivAir monitor is equipped with a variety of sensors. The centerpiece is our patented radon sensor.
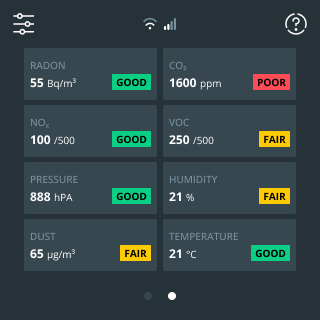
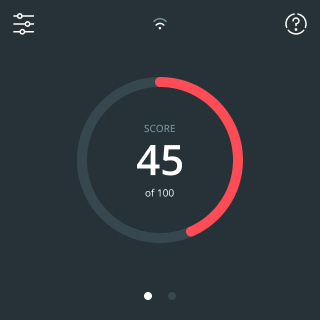
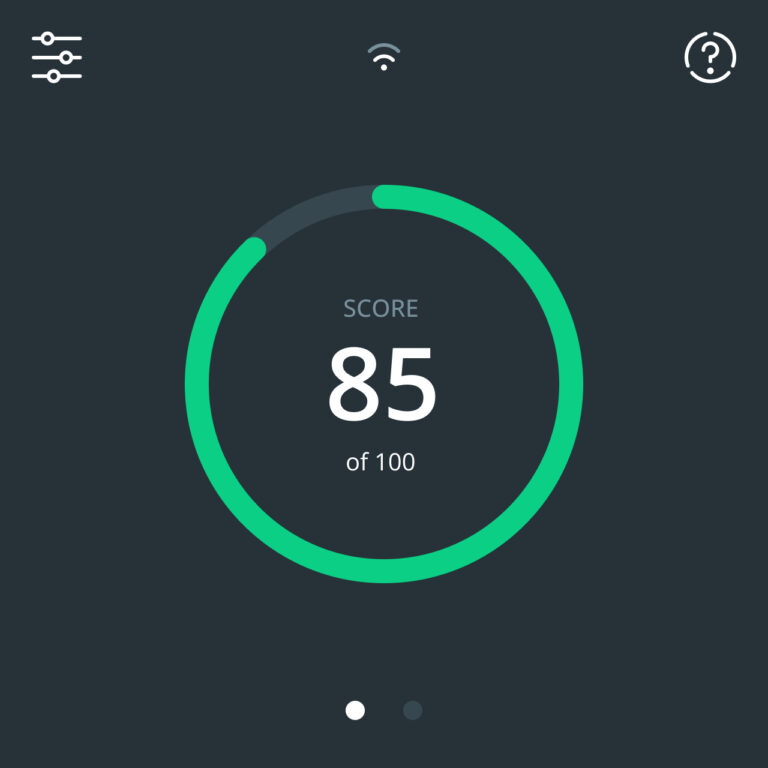

Make the invisible visible
and book your consultation now!
Take a look at how Livair ensures better indoor air.
- invest only 20 minutes of your time
- completely non-binding
- 100% Added value for you
Find out more about our other built-in sensors
Air pressure is an important factor that can affect both indoor air quality and human health.
What effects does air pressure have on human health?
Changes in air pressure can have various effects on human health. For example, low air pressure can cause the oxygen content in the air to decrease, which can lead to headaches, dizziness and breathing difficulties in sensitive people. High air pressure, on the other hand, can lead to problems with the cardiovascular system, as it can increase the strain on the heart.
Another important factor is the effect of air pressure on the body's fluid and electrolyte balance. Low air pressure can cause fluid to evaporate from the body, increasing the risk of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. High air pressure, on the other hand, can cause fluids to accumulate in the body, leading to swelling and edema.
Another important factor is the moisture content of the air. Low air pressure can cause the air to become drier, which in turn increases the likelihood of pollutants being present in the air and causing health problems.
Another important factor is the effect of air pressure on the body's fluid and electrolyte balance. Low air pressure can cause fluid to evaporate from the body, increasing the risk of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. High air pressure, on the other hand, can cause fluids to accumulate in the body, leading to swelling and edema.
How does indoor air pressure affect air quality?
Indoor air pressure can affect air quality by influencing the movement of air and pollutants in the air. Low air pressure can cause the air to stagnate and pollutants such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides to accumulate in the air. High air pressure, on the other hand, can cause pollutants to be removed quickly, improving air quality.
Another important factor is the moisture content of the air. Low air pressure can cause the air to become drier, which in turn increases the likelihood of pollutants being present in the air and causing health problems.
How can the air pressure be measured?
Air pressure can be measured using a barometer, an instrument for measuring atmospheric pressure. There are different types of barometers, including mercury barometers and aneroid barometers. Modern digital barometers can also be used to measure atmospheric pressure.
Barometers are often used by meteorologists for weather forecasts, as air pressure is an important indicator of weather conditions.











