Oxidizing gases are highly reactive gases that contribute more oxygen to combustion processes than normal air. Excess NOx concentrations cause respiratory and lung diseases as well as cardiovascular diseases (e.g. asthma, heart attacks and strokes).
Keep an eye on your NoX values. Ventilating or activating the air filter helps to lower the values.
- 351 - 500
- 151 - 350
- 0 - 150
Origin
Printers, gas heaters, tobacco smoke and fuel appliances
Effects
can cause respiratory and lung diseases as well as cardiovascular diseases
Improvement measure(s)
Increase air exchange rate
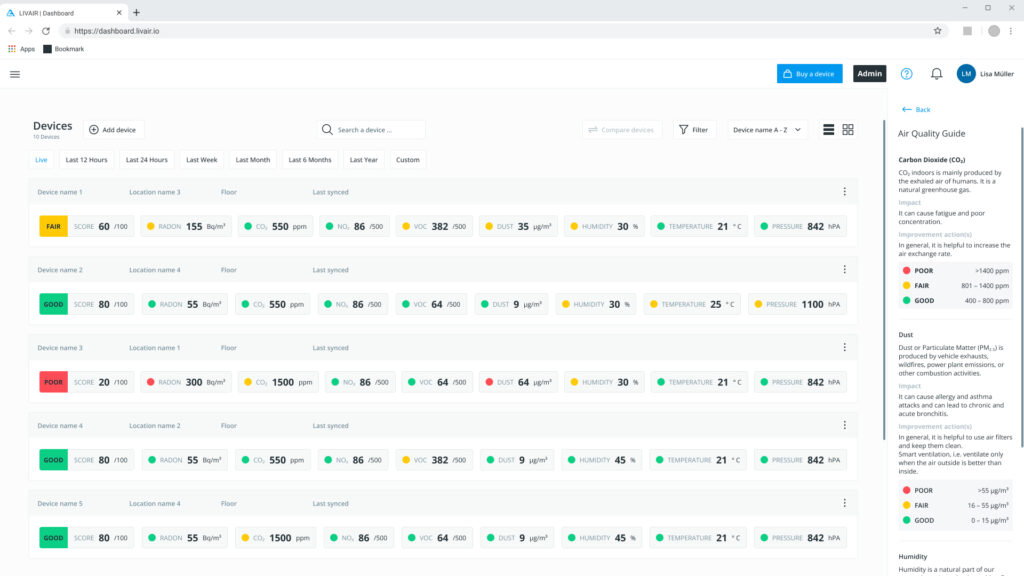

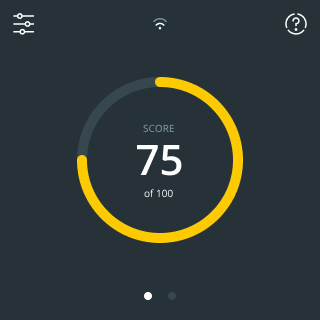
You can find all your real-time results in our dashboard with integrated air quality guide
The Air Quality Guide (AQG) is designed to help users quickly and easily classify their measured air values on a scale.
It will inform you about the origin of the relevant air factor, what effects it can have on your health and well-being and give you some general improvement measures that can work if you don't have complex problems.
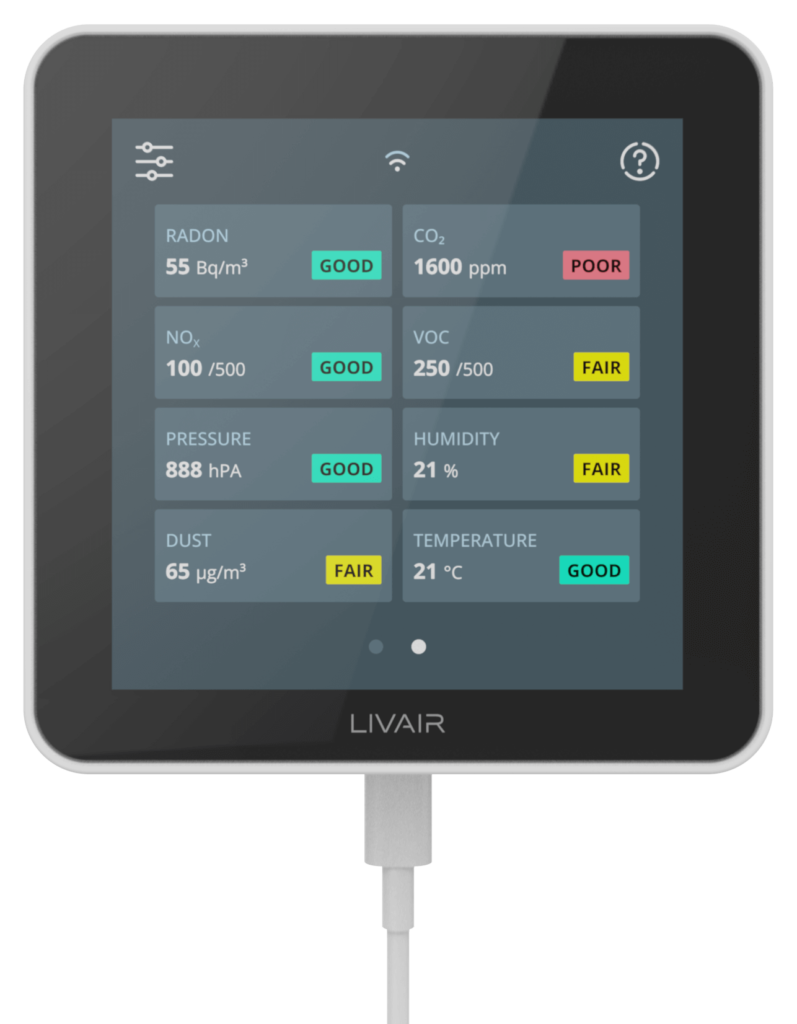
LivAir One - the most intelligent air quality monitor
The LivAir monitor is equipped with a variety of sensors. The centerpiece is our patented radon sensor.
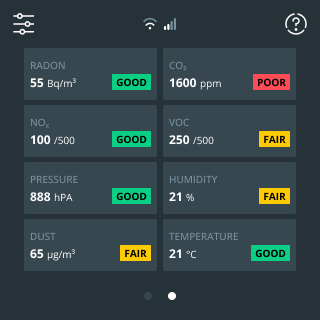
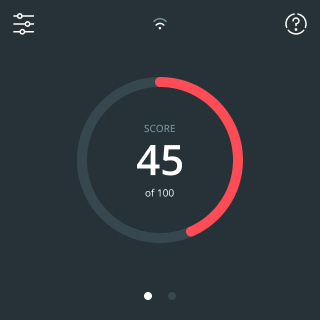
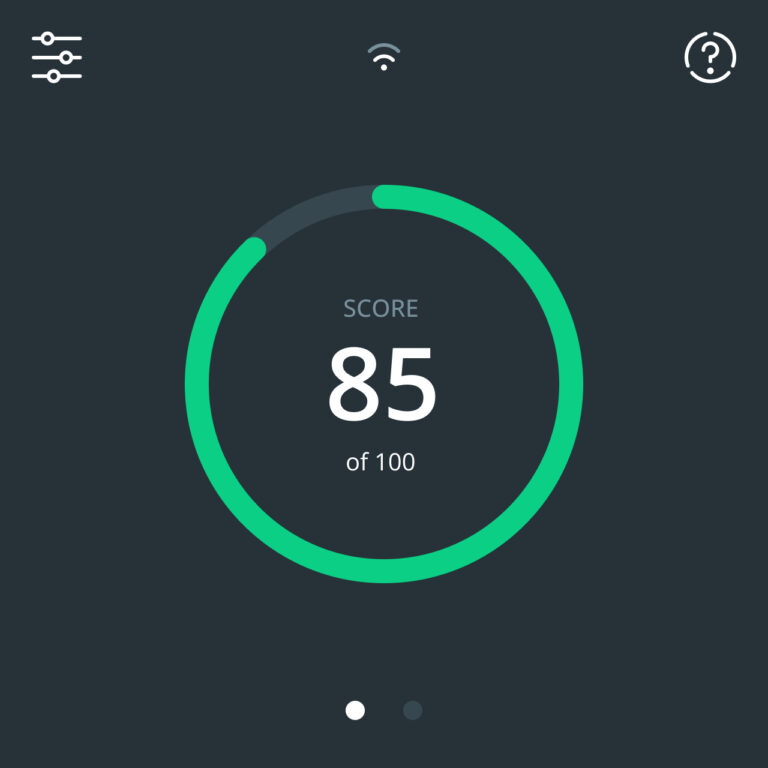

Make the invisible visible
and book your consultation now!
Take a look at how Livair ensures better indoor air.
- invest only 20 minutes of your time
- completely non-binding
- 100% Added value for you
Find out more about our other built-in sensors
NOx or nitrogen oxides are gases that are produced from the combination of nitrogen and oxygen. The most common nitrogen oxides are nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Nitrogen oxides can be released indoors from a variety of sources, e.g. gas stoves, fireplaces, cigarette smoke and traffic.
When do nitrogen oxides become dangerous indoors?
The concentration of nitrogen oxides indoors can have health effects. In high concentrations, nitrogen oxides can cause eye irritation, headaches, breathing problems and lung dysfunction. Symptoms can be more severe, especially in people with respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
How are nitrogen oxides measured?
The combination of CO2 entering the interior from outdoors, indoor breathing and the ventilation rate of a building determines the carbon dioxide concentration indoors. As buildings and homes become more energy efficient and airtight, less fresh air enters buildings and homes. To save energy, many of the ventilation systems used today recycle contaminated air instead of supplying new air. This leads to high CO2 concentrations and poor indoor air quality.
Why is it important to measure nitrogen oxides?
Measuring nitrogen oxides indoors is important to protect the health of people and pets. High concentrations of nitrogen oxides indoors can indicate potential hazards and require measures to improve indoor air quality. In addition, indoor air quality measurements can help to understand the impact of emission sources such as stoves, fireplaces and gas pipes and take action to reduce emissions.











