Cold temperatures can suppress the immune system and encourage the spread of viruses.
Set a notification so you can adjust your thermostat, or use our API to do it automatically.
- <11 °c to>31 °C
- 8 - 16 °C to 27 - 31 °C
- 17 - 26 °C
Origin
Natural seasons; heating; air conditioning
Effects
can suppress the immune system and promote the spread of viruses; can impair well-being and performance; can promote energy wastage
Improvement measure(s)
Optimize heating and air conditioning systems; ventilate if necessary; ensure appropriate work clothing
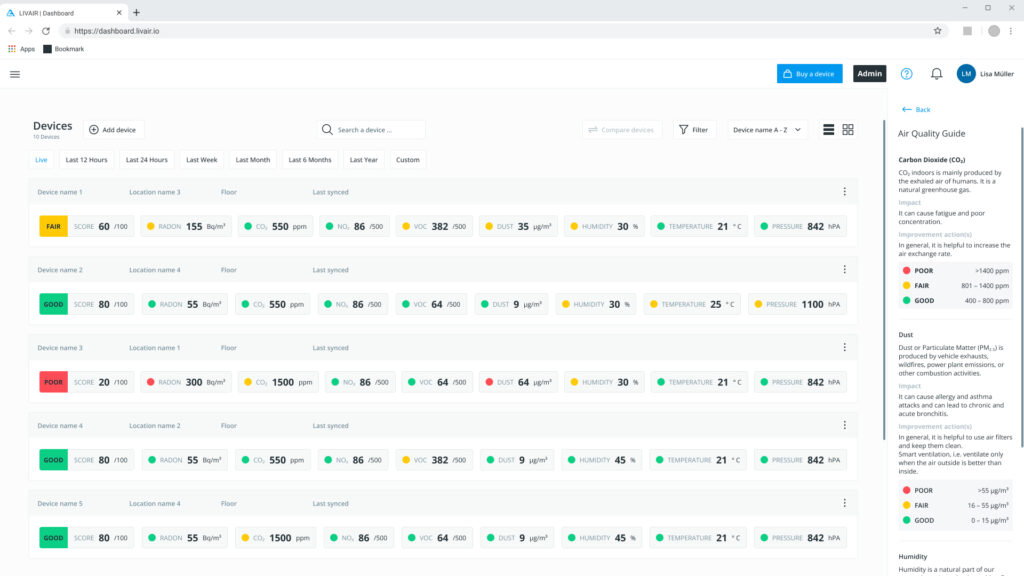

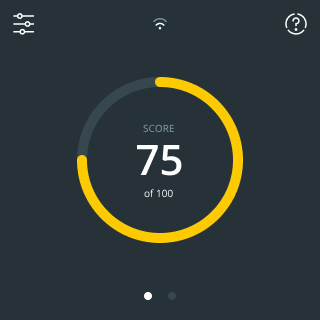
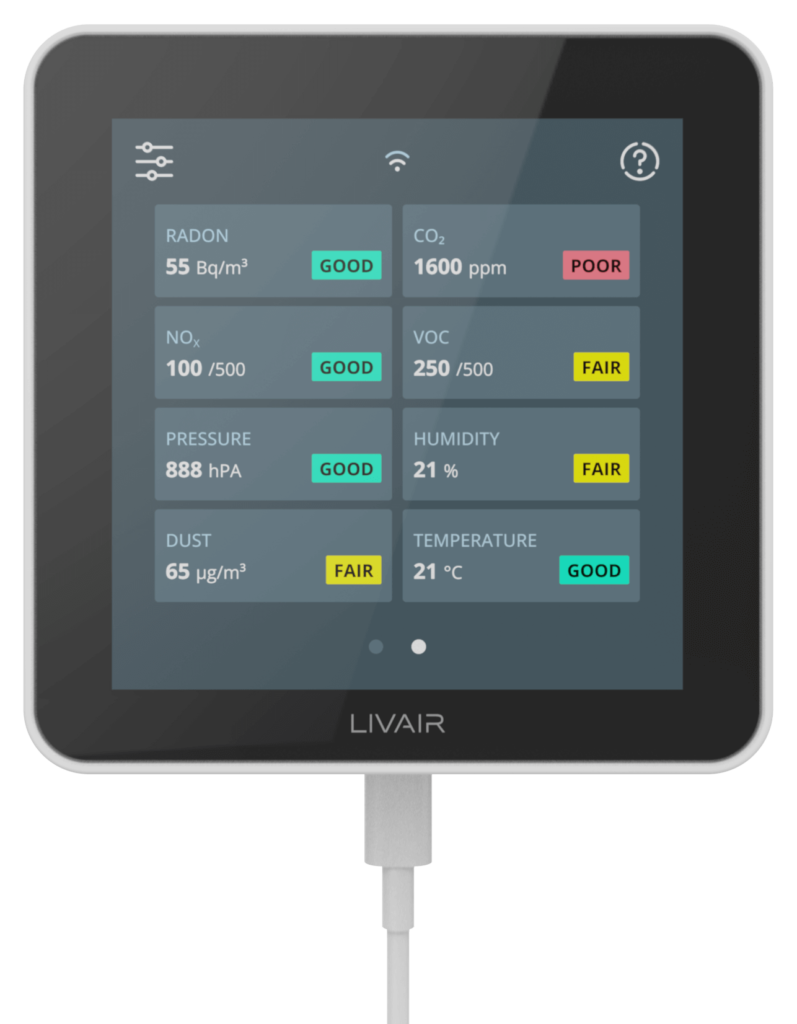
You can find all your real-time results in our dashboard with integrated air quality guide
The Air Quality Guide (AQG) is designed to help users quickly and easily classify their measured air values on a scale.
It will inform you about the origin of the relevant air factor, what effects it can have on your health and well-being and give you some general improvement measures that can work if you don't have complex problems.
LivAir One - the most intelligent air quality monitor
The LivAir monitor is equipped with a variety of sensors. The centerpiece is our patented radon sensor.
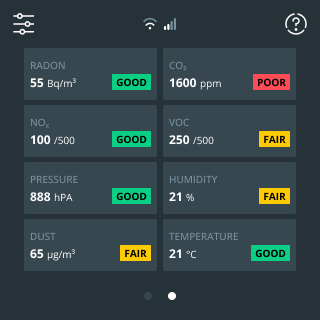
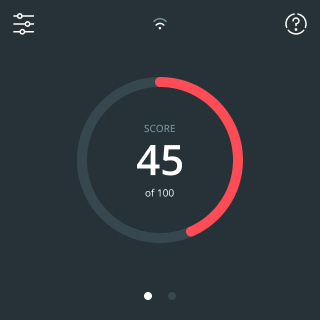
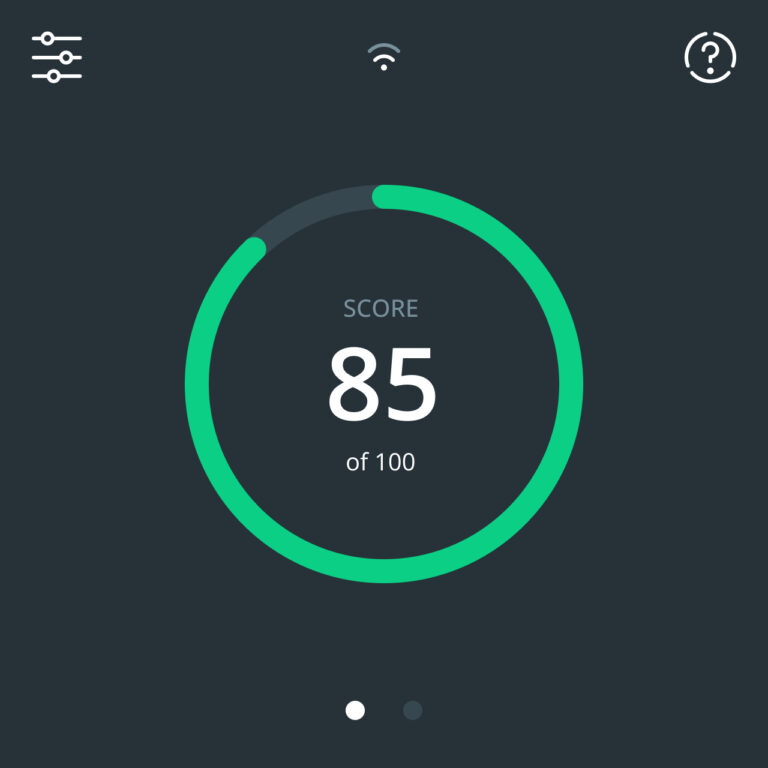

Make the invisible visible
and book your consultation now!
Take a look at how Livair ensures better indoor air.
- invest only 20 minutes of your time
- completely non-binding
- 100% Added value for you
Find out more about our other built-in sensors
Temperature is a key factor that influences our well-being and health. It also influences many other indoor air parameters such as humidity and air quality.
How do you measure the temperature?
Temperature is usually measured with a thermometer. There are different types of thermometers, including mercury, alcohol, electronic and infrared thermometers. Mercury and alcohol thermometers are commonly used in homes and medical facilities, while electronic thermometers are used in industry and laboratories. Infrared thermometers are often used for non-contact measurement of the temperature of surfaces.
The unit in which temperature is measured is degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F). Most countries use the metric system and measure temperature in degrees Celsius, while in the USA and some other countries, temperature is often measured in Fahrenheit.

What should I bear in mind with regard to the indoor temperature?
The ideal temperature indoors depends on many factors, including the time of year, the type of building and the activities that take place inside. In general, it is recommended that the temperature in living spaces should be between 18 and 24 °C. Too high or too low a temperature can lead to discomfort, health problems and higher energy bills.
It is also important to know that the temperature can vary in different parts of a room. For example, the temperature at windows or doors may be lower than in the middle of the room. This may be due to inadequate insulation or leaky windows and doors.
In buildings with air conditioning and heating systems, temperature differences can also occur if the air flow is not set correctly. It is important to adjust the air flow so that the temperature in the room is evenly distributed and there are no cold or hot spots.
What influence does the temperature have on other indoor air parameters?
Temperature has a major influence on other indoor air parameters such as humidity and air quality. At higher temperatures, the air can absorb more moisture, which leads to a lower relative humidity. Low relative humidity can cause pollutants such as dust and impurities to multiply in the air and impair indoor air quality.
A room temperature that is too high can also lead to more pollutants in the air. For example, furniture and other furnishings generally emit more volatile organic compounds (VOCs) when the room temperature is increased. These VOCs can cause health problems if they are present in high concentrations in the room air.











